For example, suppose you have a 14-slot cDAQ-9179 (USB 3.0) and want to determine whether or not it can sustain the throughput of running 14 NI-9234 modules, acquiring at the maximum sampling rate (51.2 KS/s), across all 4 channels of every device. You could calculate the total data that will be streamed across the 9179's USB bus using the equation below:
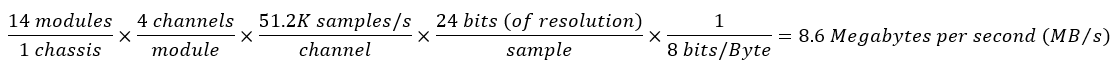
Because the total rate of data transfer during this application (8.6 MB/s) does not exceed the maximum throughput of the 9179's USB 3.0 bus (250 MB/s), there should not be bandwidth issues acquiring data at these rates on this device.
Note: The throughput calculation for Digital IO modules, such as the NI-9474, are same the as explained above, but for the Counter IO, such as the NI-9361, the data transferred from the CompactDAQ to the host PC over USB would depend on the type of measurement performed. For example when doing a edge counting task, the data returned will be a 32-bit Integer at the sample rate defined. Similarly, frequency data is a 4-byte integer and Pulse measurements are 8-byte values.