Solution
The Sample Rate of the DAQ device does not affect the accuracy of the acquired signal. The main factor in the acceptable noise from the DAQ device side is the Nominal Range we acquire the signal.
You can have a look at your device's "AI Absolute Accuracy" table by referring to its Specifications document.
For example, in the case of USB-6361, the "AI Absolute Accuracy" table is shown in the picture below.
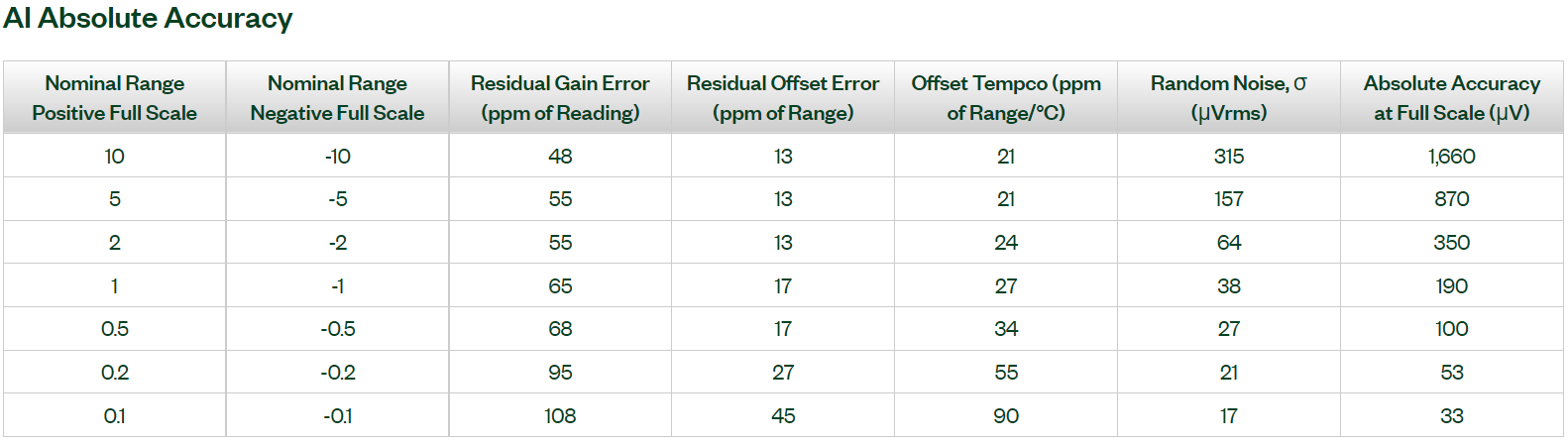
Within the Nominal Range of -5 to 5 Volts, there is an acceptable noise of 157 µVrms (~220 µV).
You can check this by running an example code from LabVIEW to continuously acquire Voltage.
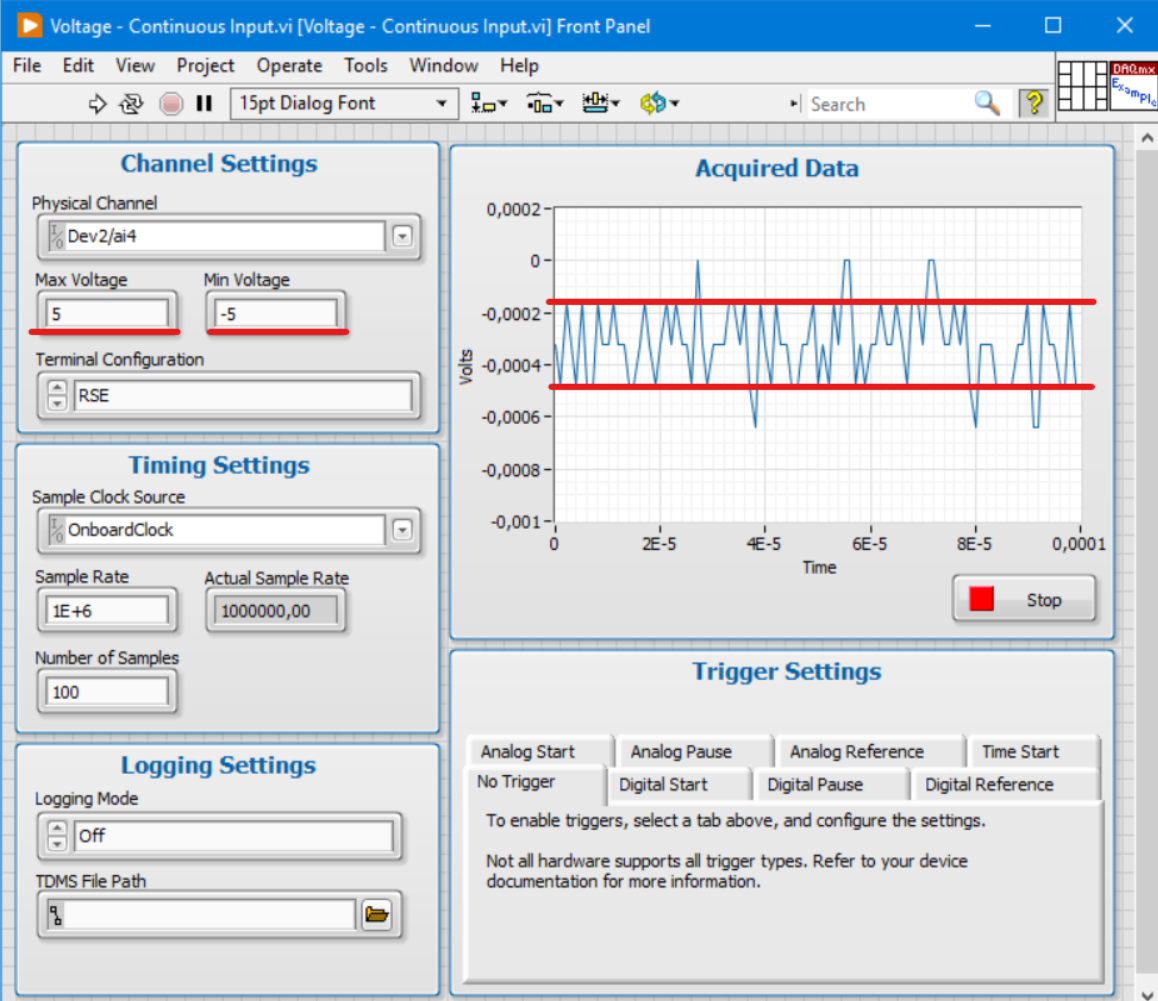
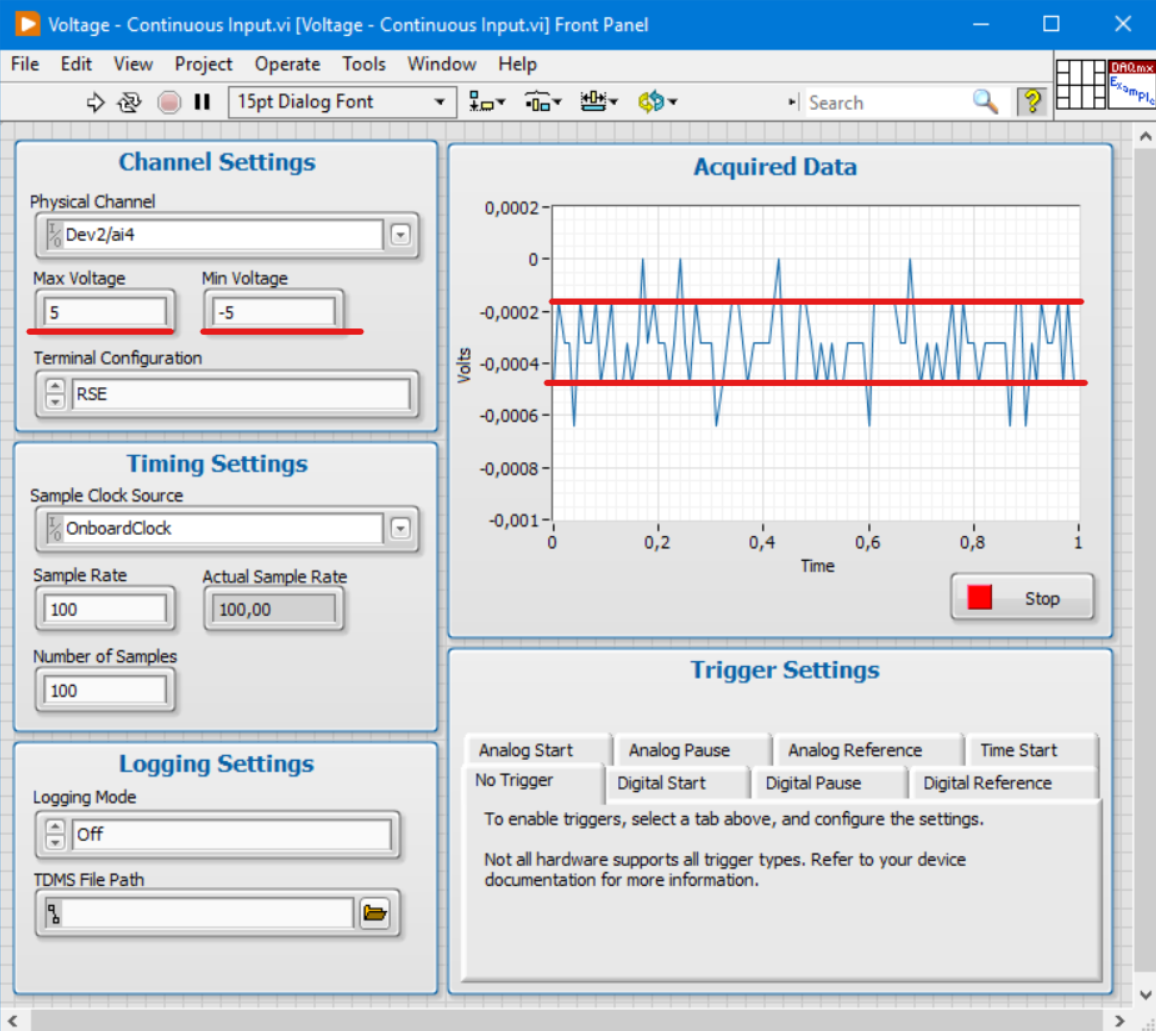
You can see that regardless of the Sample Rate the noise is the same and stays within the acceptable range (The test is done by shortcutting one of the Analog Input channels of the device).
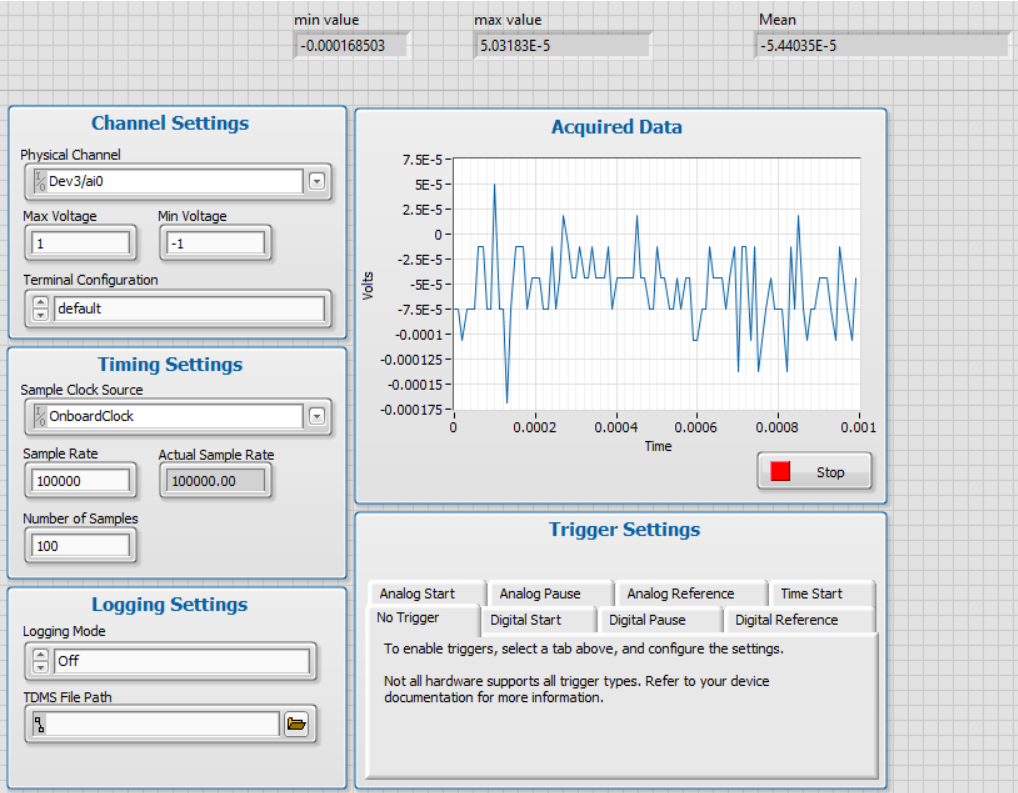
But when you change the Nominal range of the acquisition, the noise level changes as well.
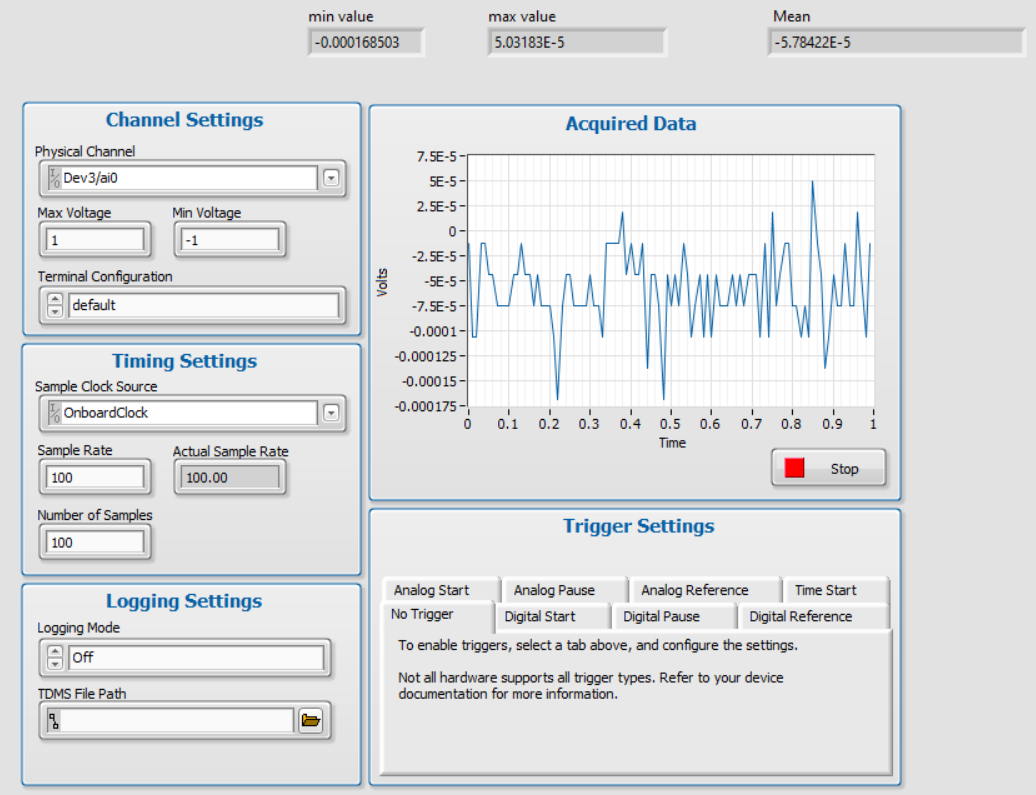
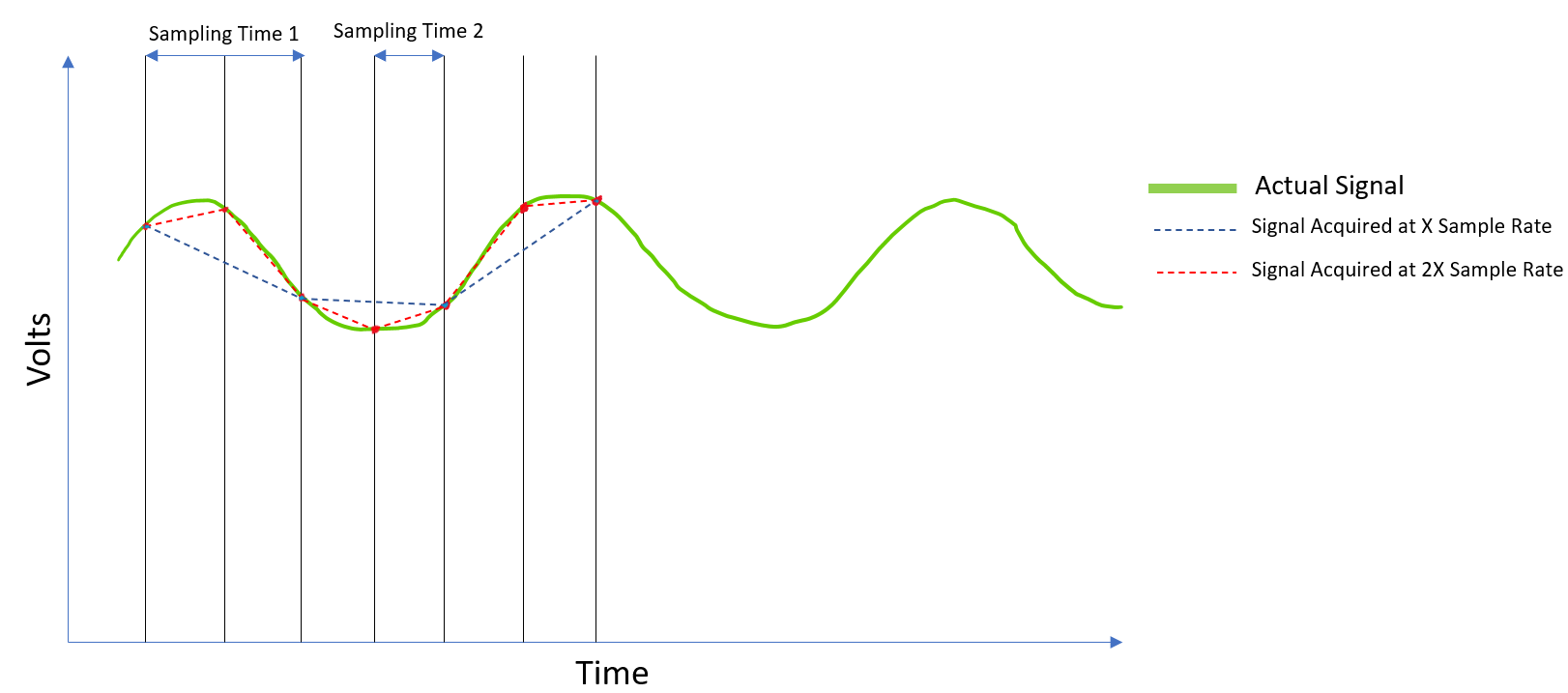
When you change the Sample Rate of the device, you choose the number of samples to acquire within one second. The ADC (Analog to Digital Converter) of the DAQ device opens and acquires one sample in the period of Sampling Time (Sampling Time = 1/Sample Rate).
The noise affecting the acquisition can vary in the range of Absolute Accuracy.
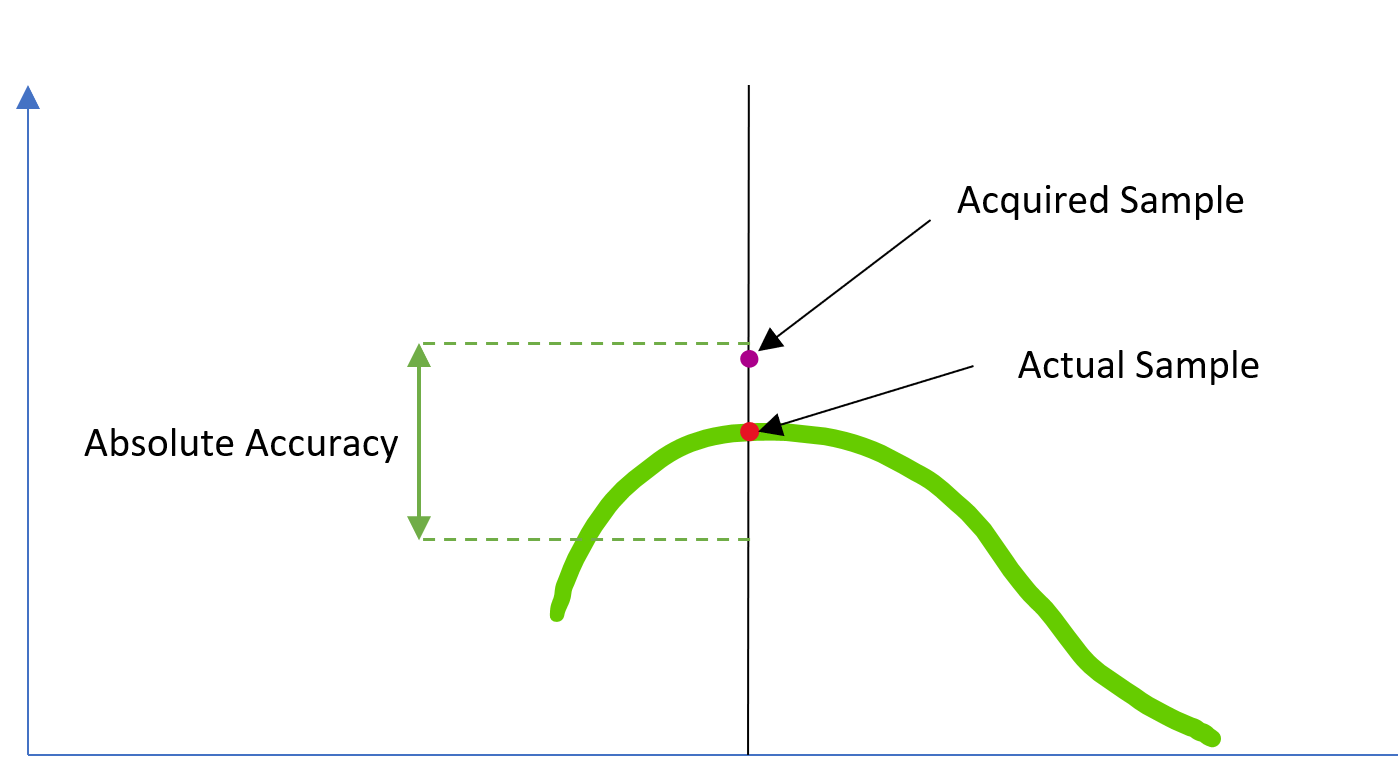
The acquired sample can vary in the range of accuracy, but the Sample Rate of the acquisition does not affect it.
The actual parameter that affects the noise level is the Nominal Range. The nominal range defines the amplifier parameters connected to the ADC. In the bigger ranges, the accuracy level is lower, thus causing more noise than in the lower nominal ranges.