System Exec VI
The
System Exec VI can be used within LabVIEW to call the Linux
shutdown command to power off the system. However, by default LabVIEW doesn't have permission to run this command so
shutdown permission must first be granted to LabVIEW by adding
lvuser, to the Linux usergroup called
shutdown.
The following steps grant LabVIEW shutdown permissions and demonstrate the LabVIEW code to power the system off:
- Open an SSH session (i.e. using PuTTY ) with the RT target.
- Run the following command: usermod -a -G shutdown lvuser
- Make sure the permission for the shutdown command was properly added to the lvuser by running the groups lvuser command.
- Reboot the target to apply changes.
- Run the shutdown command from the LabVIEW VI.
In this case, the -r parameter was used to reboot after shutting down, and now to shutdown immediately. If you need to remove the lvuser from the shutdown group later, follow these steps:
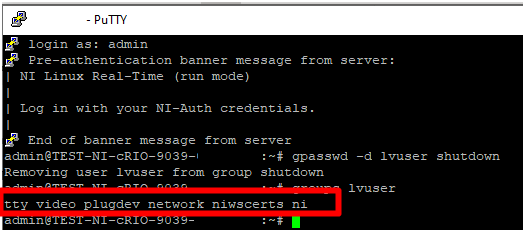
- Run the following command: gpasswd -d lvuser shutdown.
- Reboot the target to apply changes.
- Make sure the permission for the shutdown command was properly removed from the lvuser by running the groups lvuser command.
Call Library Function
You can use the
Call Library Function node to call into a standard installed library glibc on your Linux Real-Time device. Libc.so.6 is a standard Linux library utility and exists on generic Linux systems. The lvuser by default has the priorities enabled to be able to run this.
There are two ways to reference this library:
- Note that "libc.so.6" is the soname of the library and it is possible to use libc.so.6 as the path element to the Call Library Function node to load the library without needing to specify the full path. This maintains compatibility across future glibc versions.
- Alternatively, you can choose to call a specific libc.X.XX.so by a specific filepath.
An example VI of how to structure your shutdown VI is attached and will look like the following:
- This is calling into the function name "reboot" with a "cmd" I32 parameter.
- The command 4321FEDC is to shutdown the device.
If you are using a full filepath, you can check the libc-x.xx.so file that is on your device, by accessing
files >
lib (ARM) or
lib64 (Intel) >
libc-x.xx.so as shown below.
To see how to access
files on your device, refer to:
Using WebDAV to Transfer Files to Real-Time Target
Additional Information
Because of the flash-based hardware on NI Linux Real-Time devices, it is highly recommended to shut down the device before loss of battery power. You can refer to
Under the Hood of NI Linux Real-Time for more information on how to access the Linux Real-Time command line via LabVIEW.
If you wish to shut the Linux Real-Time target remotely but not programmatically, it is also possible to do this manually through SSH.