The arguments passed from the command line to the LabVIEW executable are referenced programmatically on the block diagram using the
Application:Command Line Arguments of a property node, as shown in Figure 1.
 Figure 1
Figure 1. Arguments Property Node
The arguments come in as an array of strings. The first element in the array is always the name of the application.
In LabVIEW 2019 and later,
Application Control palette includes the new Get Command Line Arguments VI (
Figure 2). This VI returns the user-defined arguments passed from the command line along with the name of the application.
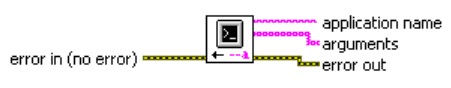 Figure 2
Figure 2. Get Command Line Arguments VI
Instructions for passing the arguments through the command line are given below.
LabVIEW 8.0 and later
With the introduction of the project in LabVIEW 8.0, you first need to enable the passing of command line arguments in the application's build specification. In order to do this follow these steps:
- Right click Build Specifications in the Project Explorer of the completed project
- Select new>>Application (EXE)
- Navigate to the Advanced category
- Check the Pass all command line arguments to application box (Figure 3)
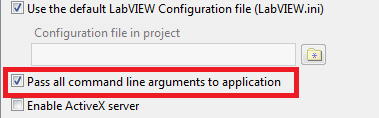 Figure 3
Figure 3. Advanced Category Check Box
To pass the command line arguments to the application and access them in your code, run the executable from the Command Prompt and add input arguments separated by spaces. For example, if
Test.exe was built, it could be called by the following, where 1000 and sine are both command line arguments:
"<build directory>\test.exe" 1000 sine
If the option to
Pass all command line arguments to application is not selected in the build specification, the application can still receive command line arguments by using the syntax for LabVIEW 7.x.
LabVIEW 7.x
User-defined arguments start after two hyphens (––) surrounded by spaces in the command line. For example, using the same LabVIEW exectuable as mentioned above;
Test.exe, it could be called by the following:
"<build directory>\test.exe" –– 1000 sine
LabVIEW 6.1 or Earlier
Windows: Use the Windows API GetCommandLine() function to read the command line which launched the current application. Parse through the string returned from the function to obtain the arguments from the command line.
UNIX: LabVIEW cannot directly read command-line arguments on UNIX systems, but it can read environment variables. Run LabVIEW with an environment variable set to the arguments you wish to pass. For example, in bash execute the following line: LVARGS="arg1 arg2 arg3" labview &. Now in System Exec VI, use echo $LVARGS as the command line string and use the returned string in your application. The same line in bash also works for a LabVIEW executable by changing Labview in the line above to the name of the executable.
For more information about using command line arguments in LabVIEW, refer to the related links below or search for "command line" in the LabVIEW Help