Solution
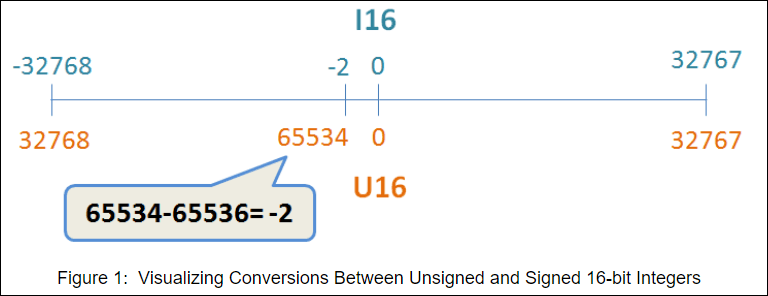
When you set the DAQmx Read Node to read Raw Data 1D arrays, you will get an array of integers. If your DAQ device has a resolution of 16 bits, you should set the DAQmx Read Node to Raw 1D U16 or Raw 1D I16 mode or you will lose effective bits. When the reading is greater than 32767 (2^15-1) in U16 mode, it means that the voltage is negative and this value is complementary code. You can convert it to a signed integer by subtracting 65536. For example, 65534 in U16 is -2 in I16. Keep in mind that unscaled Raw Data can differ between different series of DAQ cards.
M Series and X Series:
For M Series and X Series devices, the acquired raw data will be uncalibrated and unscaled. However, the calibration information and the scaling information is combined by the driver and available through the AI.DevScalingCoeff property of a Task Properties Node. This property is selected by clicking Properties » Analog Input » General Properties » Advanced » Device Scaling Coefficients. The data returned by this property is an array. Each element of the array is a coefficient of a third order polynomial which can be utilized to find a calibrated and scaled voltage:
f(X)=a[0]*X^0+a[1]*X^1+a[2]*X^2+a[3]*X^3 (where a[i] is an array element)
E Series:
For an E Series board, the acquired raw data will be calibrated on the hardware, just not scaled. The scaling information is available through the above mentioned property node. The property node will only return an array of 2 elements. This implies that the scaling of an E Series device can be represented as a first order polynomial:
f(x)=a[0]X^0+a[1]X^1
You will notice that a[0] will always be zero for an E-Series device. This also implies that a[1] is the E Series' range/resolution.
Manually Convert Binary Data to Unscaled Data:
Given the resolution of your board and measurement range, the formula below shows how to manually convert acquired binary data to unscaled data (units of volts):
Voltage Reading = (binary reading/2^bit)*(Vmax-Vmin)
Manually Convert Binary Data to Scaled Data:
Using the Device Scaling Coefficient property, you can convert the binary data to scaled data using a setup similar to the one below.