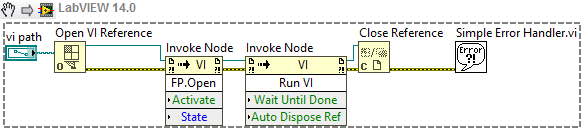
Solution
The major difference between calling by reference using the Run VI method and the Call by Reference node is the ease of programming versus the flexibility of the architecture.
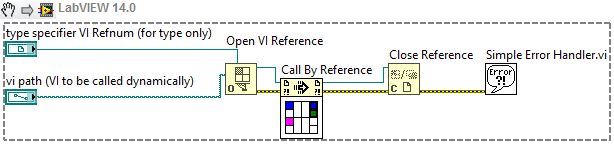
When using a
Call by Reference node you must wire in a strictly typed VI reference. A strictly typed VI reference includes connector pane information with data types as well as the reference to the VI. When using the Call by Reference Node, LabVIEW creates a connector pane for you underneath the node. With the Call by Reference node, you are able to take advantage of loading a VI dynamically, while having the convenience of simple wiring.
When you use the Run VI method, you are not required to use a strictly typed reference. As a result, you can pass any VI reference to this method to run it. Using the Run VI method allows for more flexibility, as it allows you to call VIs that do not have the same connector pane. This is a simple way to only open the Front Panel and run a VI. However,
if you want to pass values, you will need to know the names of the Controls and their data types, which requires additional programming. The Run VI method becomes more flexible because you can pass any VI path into this setup and it will be able to open and load that VI.
Another benefit of using the Run VI method over calling a VI by reference is the ability to interact with the VI. The Run VI method allows you to interact with the VI while it is running, e.g. if it needs to be controlled or in case the outputs need to be read multiple times. Using the Call by Reference node, the connector pane will output values only once, when the VI finishes execution. It does not provide the capability to interact with a running VI.