Additional Information
Some fluctuation in memory usage is expected when using non-scalar data types such as clusters, waveforms, images, or variants. This is because the size of these data types can vary during runtime.
To compensate for this fluctuation, the buffer does not contain the elements but rather pointers to the actual data. Memory for each element is then allocated dynamically at runtime as elements are written to the buffer. The dynamic allocation of memory can cause the CPU to work much harder than it needs and so it can be more efficient to use scalar data types like numerics to transfer your data instead of the non-scalar data types.
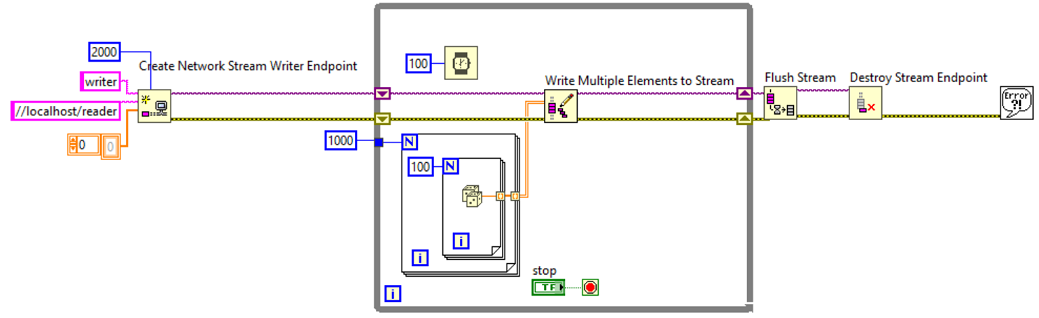
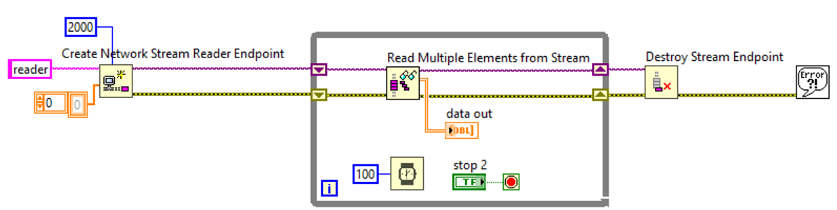
For example, it is better to use an array of doubles instead of a waveform. With the Array of Doubles, you can use the Write Multiple Elements to Stream and Read Multiple Elements From Stream functions to transfer your data across the network as in the images below. The use of the scalar values removes the need to dynamically allocate memory freeing the CPU from having to perform that operation. This decreases CPU usage while maintaining the same data rate.